Education
Nature article sheds light on next-generation fuel cell motor design
Just imagine a low-carbon "electric" vehicle that can be fully "recharged" with hydrogen in five minutes instead of with electricity that requires hours to charge. This type of fuel cell vehicle (FCV) will have a range of 800 kilometers per charge and only emit water. How can we develop the proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) that are key to FCVs? What are the technical routes?
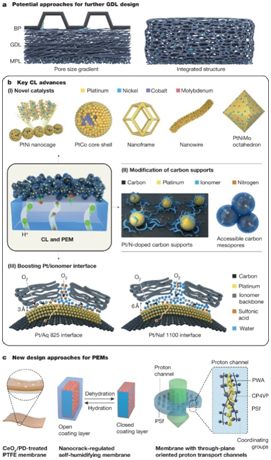
Fig. 1 State-of-the-art and next-generation MEA designs.
A research group led by Professor Jiao Kui from Tianjin University tried to answer these questions in a perspective article published in Nature, the world's leading multidisciplinary science journal on July, 14th. The 9-page long article proposes the technical development routes that are required for the development of the next-generation ultra-high power density PEMFCs.
"Many countries and regions have put forward clear development plans for fuel cells. In addition to the hydrogen related projects supported by our Chinese government, the United States, Japan and the European Union have also proposed hydrogen energy routes; planning to increase the power density of fuel cell stack to 6-9 kW/L in the next decade or so while present fuel cell models can only reach 4.4 kW/L at most," said Prof. Jiao Kui, "In the article, we addressed the current challenges and development potential involving all the components of a PEMFC, and came up with specific technical indicators through simulation calculation. Hopefully, it will help achieve the significant boost in the PEMFC stack power density.”
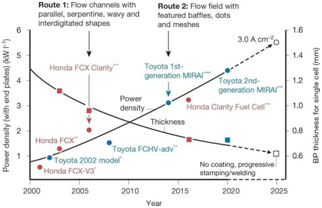
Fig. 2 Trends in the development of BPs for FCVs.
In view of the multi-scale electrochemical and thermophysical processes involved in fuel cells, the article referred to the latest achievements in the field of energy materials and analyzed the development routes of proton exchange membranes, catalyst layers, gas diffusion layers, micro-porous layers and bipolar plates of PEMFCs.
The research group also innovatively points out that the contribution of the bipolar plate and the membrane electrode assembly to future power density improvement is about 30 percent and 70 percent respectively, but the components need to be optimized to achieve the goal.
With the rapid development of fuel cell technology in recent years, the fuel cell motor using hydrogen energy has become the most attractive clean energy power option for transportation, and the one most likely to realize industrialization and commercialization. At present, major international automobile manufacturers including Toyota and SAIC have launched mass produced fuel cell vehicles, and the whole industry is going through a phase of rapid change.
The perspective article was completed under the joint efforts of Prof. Jiao Kui, Prof. Du Qing and Prof. Michael Guiver from Tianjin University, Prof. Xuan Jin from Loughborough University, UK, Dr. Hou Zhongjun from Shanghai Hydrogen Propulsion Technology Co., Ltd., and other authors from Tianjin University, Imperial College London, UK, and Shanghai Hydrogen Propulsion Technology Co., Ltd.

Copyright 1995 - . All rights reserved. The content (including but not limited to text, photo, multimedia information, etc) published in this site belongs to China Daily Information Co (CDIC). Without written authorization from CDIC, such content shall not be republished or used in any form. Note: Browsers with 1024*768 or higher resolution are suggested for this site.
Registration Number: 130349